The Tragedy Of Stuart Little
On one faithful day, StuartLittle was captured, killed, and preserved for the Biology studentsof Ms. Iannone to dissect and examine. This was the first big dissection thatmany of us done so we were all a little bit squimish and hesitant at first.When Ms. I placed the rat on our dissecting tray, my eyes lit up in wondermentand shock to see how big these animal were. Then I realized that now I getto open him up and take a look inside. The first cut was very nerve rackingbecause I did not want to cut open any organs that we needed to look at furtherthrough the dissection. However, after a few more cuts, I became moreconfident. When we opened the rat to expose the internal structures, we sawmany of the same internal structures that humans have except theenlarged livers and cecum. The knowledge of the human structure helped mygroup greatly to figure out the internals of the rat. By knowing this phylum'sinternal structure on paper, seeing it for our own personal viewing help usidentify and learn better.
Discussion Questions:
1. Why are your hands the best tools in dissection?
Hands in dissection can be the best tool to use in dissections because not only do you get to examine the feel of the part you are touching, but also it can be more accurate and easier to use when moving structures, in this case a rat, around.
2. What is the purpose of having all the different labels and titles for their dissection?
The different arrangement of labels and titles help in organizing and identifying structures and also it keeps the information accurate.
3. In what way did the tail differ from the rest of the body?
The tail of the rat appears to have scales and a bit of hair. It also felt hard and solid.
4. What purpose is served by the vibrissae?
Also known as whiskers, the vibrissae are used for tactile sensation; however, they contain no nerves inside.
5. Your specimen is bilaterally symmetrical. What does this mean?
It means that if the animal was to be cut in half, the animal would mirror the other side of the body.
6. The Sphincter is described as a circular muscle. Why is it this shape and what does it do?
The sphincter is a circular muscles and it closes and open to regulate the passing of food and this circular shape fits the tube better because the tube is a circular shape as well.
7.Why is there a difference in size between the small and large intestine?
There is a size difference because the food in the large intestine is broken down more so the food is able to be processed and passed into the small intestine where other nutrients are extracted.
8. The liver is the largest organ in the body (after the integument.) What is it's function?
It produces essential enzymes for taking in nutrients. The liver of the rat is essential for filtering contaminants from the blood and converting wastes into a disposable form. The liver converts toxic ammonia from the blood to the urine.
9. How did the duodenum acquire its name?
The duodenum (L. duodeni, twelve) was acquired this name because it literally means 12 fingerbreadths long which means 25 cm.
10. What purpose is served by the appendix in those animals that retain it as a functional organ?
It is a kind of "safe place" for certain benefical bacteria that help digest vegetables and other plant like food. Certain diseases can wipe out these bacteria. The appendix is a place where an extra supply of them are stored.
11. In each of the cavities, there is a membrane that covers both the wall of the cavity and the organ it contains. What is the function of the membrane?
The membrane is vital because it separates layers, lubricates the surface, for tension and protection.
12. What is the function of the spleen?
The spleen is a blood cleaner that contains white blood cells that destroy used up, old red blood cells.
13. What is the function of the diaphragm?
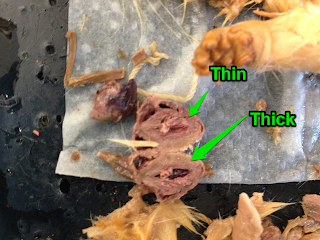
The Diaphragm has many functions but the main function is that is helps in respiration and breathing but contracting and expanding. The diaphragm helps air to exit and enter the lungs.14. What distinguishes the atria from the ventricles?
The atria are smaller than the ventricles and consists of thinner muscle tissues than lower positioned ventricles. The atria also pumps blood to the ventricles while the ventricles distribute oxygenated blood around the body. The ventricles are also larger in size due to their complex job.
15. Why is the wall of the left ventricle thicker than that of the right?
The left ventricle is more muscular because it has to pump blood at a higher pressure to further distances.
16. What are the similarities exist between male and female reproductive systems?
 Both female and male reproductive systems appear very different; however, one attribute that they both share is a pituitary gland.
Both female and male reproductive systems appear very different; however, one attribute that they both share is a pituitary gland.17. What do the kidneys do?
Kidneys in rats help to make waste OK to excrete along with regulating the balance of water in the body.
18. In the dissection, you located the thyroid, the thymus, and the adrenal glands. To which system do they belong to?
This structures are apart of the respiratory system.
Here is a little overview: